Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Support for educating learners with autism
- Educational Placement Opportunities for Autism in Schools
- Pre-Employment Transition Services:
- Employment Opportunities for People with Autism:
- Resources and Links to Federal and Private Employment Programs:
- Conclusion
- Did You Know About Folate Receptor Autoantibodies (FRAAs) and Brain Development?
- References
Introduction
If you or a loved one have autism, you may be wondering what options are available for education and employment. We understand that navigating these opportunities can be overwhelming, which is why we’ve compiled this guide to help you explore the various paths available.
Whether you’re a student with autism looking to pursue higher education or a parent seeking employment options for your child with autism, we hope this blog post will provide valuable insights and resources to help you make informed decisions. So, let’s dive in and explore the education and employment opportunities for people with autism.
Individuals with autism can face various challenges when it comes to learning, such as difficulty with social communication, sensory processing, and executive function. However, it’s important to recognize that individuals with autism also have unique strengths, such as attention to detail, strong visual processing abilities, and a deep focus on their interests. Understanding these challenges and strengths is crucial in developing effective educational strategies for learners with autism.
Support for educating learners with autism
- Several evidence-based approaches are effective in educating learners with autism, such as:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Naturalistic teaching strategies
- Structured teaching approaches
It’s important to note that every individual with autism is different and may respond differently to different approaches, so it’s crucial to develop an individualized education plan (IEP) that meets their specific needs and goals.
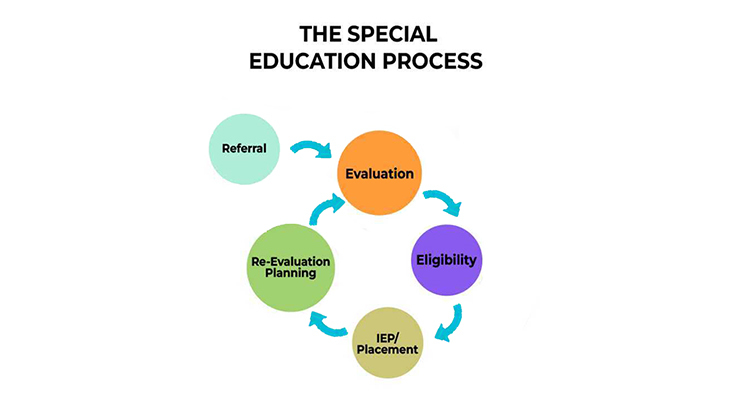
- Additional support is provided through the special education team in schools after evaluation. This can include:
- Speech and language therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Physical therapy
- Assistive technology:
Technology such as communication devices, tablets, and specialized software can be used to help minimally verbal students with autism learn and communicate effectively.
Educational Placement Opportunities for Autism in Schools
In recent years, there has been a growing movement towards inclusive education, where learners with autism are integrated into mainstream classrooms and given the support they need to succeed. There are many programs and resources available that promote inclusive education, such as Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS). In addition, organizations and advocacy groups provide support and resources to families and educators of learners with autism, such as Autism Speaks and the Autism Society of America.
Currently, after evaluation schools provide students with the following placement opportunities:
- Inclusive classrooms:
Inclusive classrooms are designed to integrate students with autism into mainstream classrooms with the necessary support and accommodations to facilitate learning. - Reverse Inclusion:
Students from mainstream classrooms are included in the special education classrooms for a few classes to help promote inclusion opportunities. - Co-teaching classrooms:
Classrooms with a teacher and special education teacher are known as Co-teaching classrooms. Kids with special needs like autism and other conditions are taught with their neurotypical peers. - Self contained classrooms:
Autistic children needing further care and focused instructions are placed in the self-contained classroom. They have a low teacher-student ratio with paraprofessionals assisting the children with their educational and daily needs.
Pre-Employment Transition Services:
Both vocational rehabilitation agencies and schools are required by law to provide certain transition services and support to improve post-school outcomes of students with disabilities like autism spectrum disorder.
The IEP has to outline the specific steps of the transition plans for work or secondary education and provide corresponding services for the student with autism to attain the goal. This is done through age-appropriate vocational services assessments through qualified professionals.
The intent of pre-employment transition services is to improve the transition of students from school to postsecondary education or to an employment outcome.
Pre-employment transition services include:
- Job Exploration Counseling
- Work-Based Learning Experiences
- Counseling on Postsecondary Education Opportunities
- Workplace Readiness Training
- Instruction in Self-Advocacy
Employment Opportunities for People with Autism:
Individuals with autism often face barriers in the job market, such as difficulty with social interaction and communication, sensory sensitivities, and a need for routine and predictability. These barriers can make it challenging for individuals with autism to find and maintain employment. However, there are also opportunities for individuals with autism in the job market, particularly in fields that require attention to detail, strong visual processing skills, and specialized knowledge in certain areas.
- Benefits of hiring individuals with autism:
There are several benefits to hiring individuals with autism, including increased productivity, reduced turnover, and enhanced diversity and creativity in the workplace. Individuals with autism may also bring unique perspectives and problem-solving skills to the workplace, which can lead to innovation and improved outcomes. - Workplace accommodations:
Employers are required to provide reasonable accommodations to employees with disabilities, including those with autism. This can include flexible work schedules, modified job duties, and assistive technology.
Resources and Links to Federal and Private Employment Programs:
- Each state has a Vocational Rehabilitation (Vocational Rehab or VR) agency that provides employment service supports to people with disabilities (including autism). VR is paid for by the federal and state government. It is available in every state to help people with disabilities prepare for and obtain jobs. Find your State Vocational Rehabilitation (VR) Agency here. A report from the Drexel University study on VR highlights the issues and outcomes for Autism.
- Directory of government and private organizations that offer resources or support for job seekers with disabilities and employers
- Employer Assistance and Resource Network on Disability Inclusion (EARN)
- Job Accommodation Network
- National Collaborative on Workforce and Disability for Youth (NCWD/Youth)
- Partnership on Employment & Accessible Technology (PEAT)
- Project SEARCH: Project SEARCH was developed at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. The idea was to train people with developmental disabilities to fill some of the high-turnover, entry-level positions, which involved complex and systematic tasks such as stocking supply cabinets.
- Microsoft Neurodiversity program
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you or someone you know has autism, it’s important to know that there are many support services available to help children and adults with autism succeed in education and employment. Whether it’s through special education programs, vocational training, job coaching, or workplace accommodations, there are resources and organizations dedicated to providing the necessary support and accommodations to help individuals with autism reach their full potential. By taking advantage of these opportunities and seeking out the appropriate resources, children with autism can thrive in the classroom and the workplace, and go on to lead fulfilling and rewarding lives.
For information on autism monitoring, screening and testing please read our blog.
References
- https://childmind.org/article/autism-and-employment/
- https://lexingtonservices.com/career-paths-for-people-with-autism/
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/things-you-need-to-know-about-autism-and-employment-4159850
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/juliabrodsky/2021/04/07/how-people-with-autism-can-find-training-and-jobs/?sh=31f139f841bb
- https://www.autismparentingmagazine.com/best-autism-jobs-and-careers/
- https://www.iidc.indiana.edu/irca/articles/choosing-the-right-job-for-people-with-autism-or-aspergers-syndrome.html
- https://www.leicspart.nhs.uk/autism-space/education-and-employment/autism-and-the-transition-from-education-to-employment/
- https://psychcentral.com/autism/jobs-for-autistic-people